Types of gemstones
Gemstones have captivated cultures throughout history with their beauty, symbolism, and perceived powers. These natural minerals are mainly classified into precious and semi-precious gemstones. Precious stones—diamonds, rubies, sapphires, and emeralds—are prized for their rarity, brilliance, and historical value, making them the most sought-after. Semi-precious stones, like amethyst, garnet, and turquoise, offer beauty and variety but are generally more common and accessible. This distinction, rooted in tradition, reflects differences in rarity, luster, and color intensity, which influence their desirability and value in the gemstone market.
Color Intensity and Quality
Precious Gemstones: Precious stones like rubies, sapphires, emeralds, and diamonds are often prized for their deep, vivid, and highly saturated colors. For example, the rich “pigeon blood” red of rubies or the deep blue of sapphires is rare and highly sought after. The colors are usually uniform and intense, contributing to their high value.
Semi-Precious Gemstones: While some semi-precious stones have beautiful colors, they often lack the uniform saturation seen in precious gems. Stones like amethyst, citrine, and peridot can have striking colors, but they may be lighter, less intense, or more variable in hue.
Clarity and Texture
Precious Gemstones: These stones tend to have superior clarity, with fewer inclusions or imperfections, especially in high-quality specimens. While some, like emeralds, often have inclusions, these are sometimes valued as part of their character (e.g., “jardin” in emeralds). Precious gemstones also generally have a smoother, more lustrous texture when polished.
Semi-Precious Gemstones: Semi-precious stones often have more inclusions, internal fractures, or variations in clarity. For example, stones like garnet or tourmaline can have visible inclusions or uneven color distribution. Their texture, while still appealing, may be less lustrous or more prone to flaws compared to precious stones.
Optical Effects
Precious Gemstones: High-quality precious stones exhibit superior brilliance, fire (dispersion of light into rainbow colors), and sparkle. Diamonds, for instance, are renowned for their exceptional light performance.
Semi-Precious Gemstones: While some semi-precious stones like opal and moonstone display unique optical effects (e.g., play-of-color or adularescence), these effects are different from the brilliance and fire seen in diamonds and other precious gems.
Precious Gemstones

DIamonds

Sapphires

Emeralds

Rubies
Diamond
Color: Colorless to various shades (yellow, pink, blue, etc.)
Characteristics: Known for its exceptional hardness (10 on the Mohs scale) and brilliance. Diamonds are valued for their clarity, cut, and color
Sapphire
Color: Primarily blue, but can occur in various colors including pink, yellow, and green (excluding red, which is classified as ruby)
Characteristics: Another variety of corundum, sapphires are prized for their hardness (9 on the Mohs scale) and color. Blue sapphires are the most famous, but fancy sapphires in other colors are also highly valued.
Ruby
Color: Various shades of red, from pinkish to deep red (often termed “pigeon blood red”)
Characteristics: A variety of corundum, valued for its intense color and hardness (9 on the Mohs scale). Rubies are known for their rich, vivid hues and are often used in high-end jewelry.
Emerald
Color: Green, ranging from light to deep green
Characteristics: A variety of beryl, known for its distinct green color and moderate hardness (7.5 to 8 on the Mohs scale). Emeralds are often valued for their vibrant green hue and historical significance, despite commonly having inclusions.
Primary Semi-Precious Gemstones

Amethyst

Garnet

Citrine

Topaz

Peridot

Aquamarine

Tourmaline

Moonstone
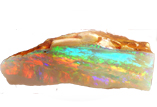
Opal
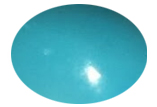
Turquoise

Lapis Lazuli

Jasper

Onyx

Chrysoprase

Labradorite

Sardonyx

Malachite

Spinal
While there are hundreds of semi-precious gemstones in the world, we’ve curated this list to focus on the 18 types that are most popular and widely used in jewelry and decorative pieces. These selections include stones that offer the best combination of beauty, availability, and market demand. By concentrating on these key gemstones, we ensure that our customers have access to the most versatile and sought-after options, ranging from timeless classics to trendy favorites.
Amethyst
Color: Purple, ranging from light lavender to deep violet
Characteristics: A variety of quartz, popular for its wide range of purple hues.
Garnet
Color: Red, but also found in green (tsavorite), orange (spessartite), and other colors
Characteristics: Includes several varieties such as almandine, pyrope, and tsavorite.
Citrine
Color: Yellow to golden brown
Characteristics: A variety of quartz, often used as a more affordable alternative to yellow diamonds.
Topaz
Color: Ranges from clear to various shades of blue, yellow, and pink
Characteristics: Known for its clarity and vibrant colors, with blue topaz being particularly popular.
Peridot
Color: Olive green to yellow-green
Characteristics: Known for its bright green color and is one of the few gemstones that occur in one colo
Aquamarine
Color: Light to medium blue, sometimes with a greenish tint
Characteristics: A variety of beryl, valued for its clear, pale blue color.
Tourmaline
Color: Comes in a wide range of colors including pink, green, and blue
Characteristics: Includes various types like pink tourmaline, green (chrome) tourmaline, and the rare Paraíba tourmaline.
Moonstone
Color: Colorless to white, with an iridescent play-of-color
Characteristics: Known for its adularescence (a soft glow that seems to move across the surface).
Opal
Color: Various colors, often with a play-of-color effect (e.g., black opal, fire opal)
Characteristics: Unique for its ability to display multiple colors and patterns.
Turquoise
Color: Blue to green
Characteristics: An opaque gem known for its distinctive color and use in various cultures.
Lapis Lazuli
Color: Deep blue with gold flecks (pyrite) and white veins (calcite)
Characteristics: Valued for its rich blue color and historical significance.
Jasper
Color: Found in a variety of colors and patterns
Characteristics: An opaque, often multicolored or patterned variety of chalcedony.
Onyx
Color: Typically black, but also available in various colors and patterns
Characteristics: Known for its smooth, glossy finish and consistent color.
Chrysoprase
Color: Bright green
Characteristics: A variety of chalcedony with a vivid green color due to nickel content.
Labradorite
Color: Gray to dark brown with iridescent flashes of color (known as labradorescence)
Characteristics: Valued for its unique optical effect.
Sardonyx
Color: Alternating bands of sard (reddish-brown) and onyx (black or white)
Characteristics: Known for its banded appearance and use in cameo carvings.
Malachite
Color: Bright green with distinctive banding
Characteristics: Often used in decorative pieces and jewelry.
Spinel
Color: Available in a wide range of colors including red, pink, blue, and black
Characteristics: Known for its brilliance and is often mistaken for ruby or sapphire.
Fine Jewlery Collections
- Fine Jewelry From Our Atelier
- Custom Designed & Crafted Jewelry
- Unity Collection
- Diamond Bracelets & Bangles
- Diamond Necklaces
- Google Merchant Products
- Wedding & Eternity Bands
- Diamond Engagement Rings
- Diamond Pendants
- Diamond Earrings
- Black Diamond Jewelry
- Diamond & Gemstone Cufflinks
- Video Galleries
- Videos - Diamond Rings
- Videos - Diamond Tennis Bracelets
- Videos - Diamond Eternity Bands
- Videos - Diamond Earrings
- Videos - Black Diamonds & Gemstones
- Video Gallery - Fancy Colored Diamonds
DIAMOND/GEMSTONE EDUCATION
- Jewelry Education Hub
- What Are Diamond Certificates?
- Difference Between Certificates
- Laser Inscribed Diamonds
- Learn About Diamonds – The 4C’s
- Diamond Carat Weight
- Diamond Color
- Diamond Clarity
- Diamond Cut
- Diamond Polish
- Diamond Symmetry
- Diamond Sizes in MM
- Know Your Ring Size
- Understanding Gemstones
- Types Of Gemstones
- Precious Gemstones - Rubies, Sapphires and Emeralds
- Sapphires
- Rubies
- Emeralds
- Treatments & Enhancements
- Birthstones and Their Significance
- Gemstone Grading
- Lapis Lazuli
GENERAL INFORMATION
- MyAntwerpDiamonds Information
- Terms and Conditions
- Contact MyAntwerpDiamonds.com
- Refund Policy
- Customer Reviews
- Shop with Confidence
- Purchase Pointers
- Shipping Information
- VAT Refunds and VAT Free Diamond Jewelry
- USA – Tax Free Diamond Jewlery
- UK – Tax Free Jewelry
- Switzerland – Tax Free Diamond Jewelry
- Australia – Tax Free Diamond Jewlery
- Privacy & Cookies Policy
- User Account
MyAntwerpDiamonds.com /
- sales +32 473 21 02 44
- sales +32 473 21 02 44
- administration +32 3 231 1643
- SUPPORT@myantwerpdiamonds.com
- NV JOAILLERIE FRÈRES FROHMANN, Pelikaanstraat 54, 2018 Antwerp, Belgium
Some email responses from us may be filtered as spam or blocked altogether. To ensure you receive our emails, please provide your telephone or WhatsApp number for verification.



